Essential Strategies for Enhancing First Responder Communication in Remote Locations
Reliable communication is the backbone of effective emergency response. In remote areas, where infrastructure is lacking, communication challenges can impede law enforcement, private security, military, and emergency management teams. In these settings, strong communication networks can mean the difference between life and death.
This article looks at the main problems of communication in remote areas. It also suggests ways to help first responders stay connected.
Understanding the Challenges of Remote Communication
First responders face unique communication obstacles in remote areas that can complicate their operations. These obstacles primarily relate to the environment and the available infrastructure.
- Geographical Barriers: Natural features like mountains, forests, and wide-open deserts can weaken communication signals. This can make it hard to maintain contact between teams.
- Lack of Infrastructure: Remote locations often don’t have built-in communication infrastructure such as cell towers or two-way radio networks.The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) says that at least 14.5 million Americans do not have broadband access. Many of these areas are remote or rural. This lack of infrastructure is a critical challenge for first responders operating in these regions.
- Power Limitations: Without a reliable power source, communication devices may fail, leaving first responders unable to communicate effectively. Battery-powered devices need recharging, and generators can be cumbersome to transport.
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, 83% of major power outages from 2000 to 2021 were weather-related. U.S. electricity customers experienced an average of seven hours of power interruptions in 2021, significantly impacting communication systems during emergencies.
These challenges can slow down response times. They can also raise risks. This makes it hard for teams to work together on rescue efforts. Addressing these issues requires innovative, portable solutions that can work in tough environments.
Real-World Examples of Communication Failures
There have been real-world cases where inadequate communication in remote areas impacted emergency response efforts:
- Hurricane Katrina (2005): During Hurricane Katrina, the collapse of communication systems—including downed cell towers and failed radio frequencies—left first responders without critical tools for coordination. This led to significant delays in rescue operations.
- Mount Rainier Rescue Operation (2012): In this mountain rescue, limited communication infrastructure made it challenging for search teams to coordinate. They brought in portable radio towers to help extend the range of their radios. This allowed for a successful rescue of the stranded hikers.
These incidents highlight the importance of having reliable communication systems in place, especially in disaster-stricken or rugged terrains.
Geographical Barriers and Their Impact
Remote areas often have rugged landscapes that block or weaken signals. Here’s how different terrains can interfere with first responders’ communication systems:
- Mountains: Signals struggle to travel through rock formations. This makes it difficult for teams to stay connected when separated by hills or mountains.
- Dense Forests: Thick vegetation blocks radio waves, which can disrupt communication between teams spread across large forested areas.
- Wide-open Plains: Although flat, these areas often lack the necessary infrastructure to support communications, leaving responders without reliable connectivity over vast distances.
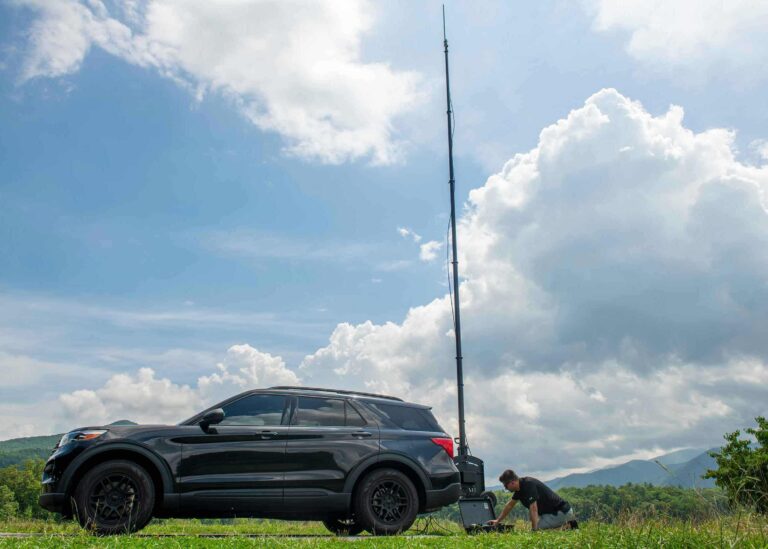
To overcome these challenges, specialized communication technologies, such as telescopic masts, can provide the elevation needed to bypass obstructions and extend communication coverage.
Limited Infrastructure and Resource Constraints
Remote locations usually lack cell towers, communication hubs, or even power lines. First responders in these areas need to set up temporary networks. This can be difficult because they face challenges of limited resources and staff.
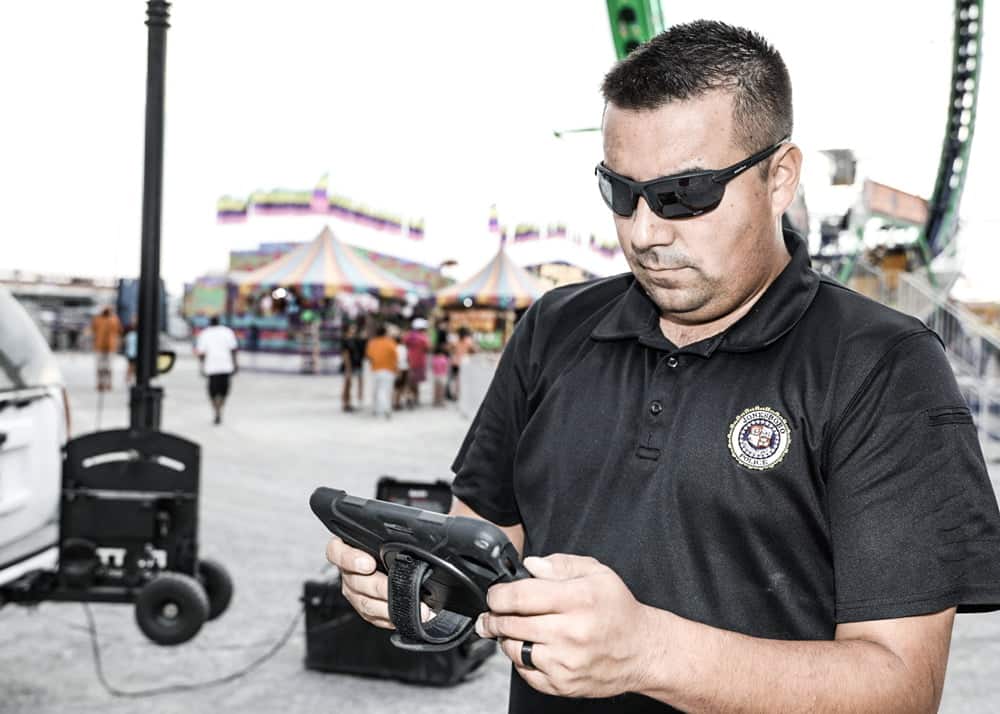
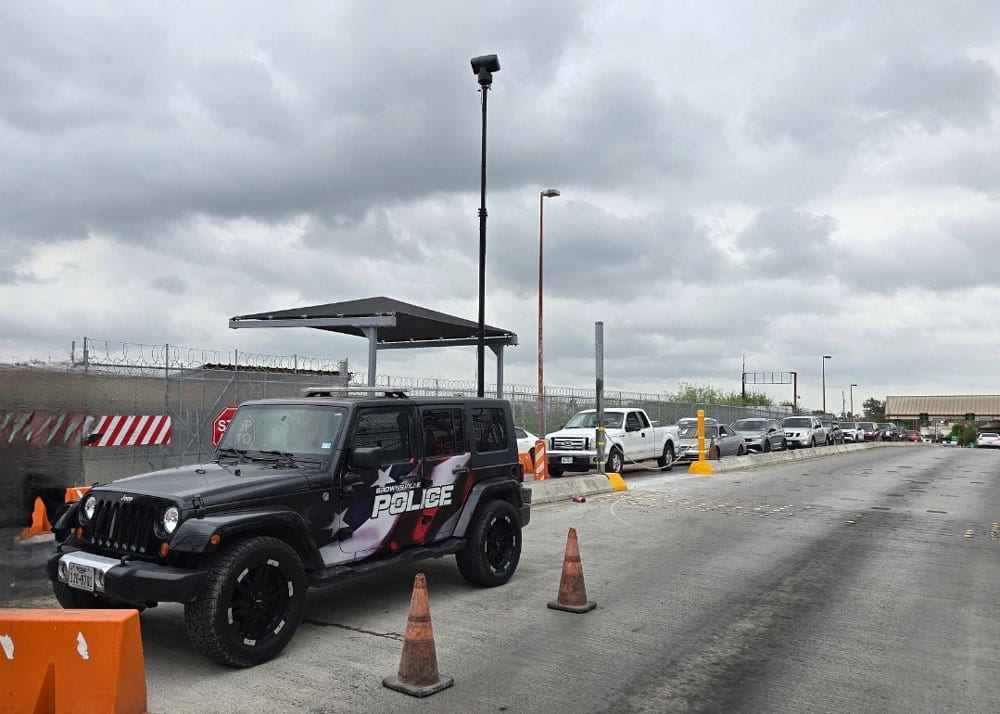
In these cases, mobile surveillance towers are very important. They offer a way to set up communication tools, cameras, and lights. These towers are especially useful for teams that need to set up quickly in the field.
Additionally, establishing reliable power sources is critical. People often use devices such as portable generators or solar panels, but they require careful planning and logistics. Without proper infrastructure or resources, teams can struggle to maintain consistent communication, making emergency response more difficult.
Using Wireless Technology for Improved Coverage
Wireless technology is crucial for remote areas. By bypassing traditional infrastructure, first responders can maintain contact over longer distances and in areas where regular communication systems fail.
- Satellite Phones: Satellite phones are vital for maintaining communication in places where no cell towers exist. This offers reliable global coverage by connecting directly to orbiting satellites. It also ensures connectivity even in remote or disaster-affected areas where traditional networks fail. However, they come with challenges such as higher costs and vulnerability to signal delays, particularly in adverse weather conditions.
- IP Cameras: For security personnel, the use of IP cameras enables surveillance in remote locations. These cameras can connect to mobile surveillance towers to provide aerial views. This offers situational awareness even in hard-to-reach areas. This makes them highly effective for emergency response teams operating in remote regions.
Implementing Mobile Surveillance Units
For first responders, having the ability to deploy surveillance rapidly is a game-changer. Mobile surveillance systems help teams watch large areas in real time. They collect important information to support operations.
Teams can deploy mobile surveillance towers quickly, providing critical 360-degree coverage in remote areas. Law enforcement agencies often use them in wilderness areas or during large outdoor events to monitor crowd movements and prevent incidents.
Light towers and telescopic masts improve visibility and communication in dark places or areas lacking infrastructure. These tools provide essential support in environments where permanent infrastructure is unavailable.
Utilizing Mesh Networks for Expanded Connectivity
A mesh network offers a flexible, scalable way to extend communication reach. In a mesh network, devices connect with each other, forming a web that increases coverage over a wide area.
- Portable Mesh Devices: Battery-powered mesh nodes can be easily transported and set up in remote locations. This creates a temporary communication grid.
- Ad-hoc Networks: Mesh networks work particularly well in emergencies where traditional communication infrastructure may be damaged or unavailable. This provides continuous coverage when you add nodes.
Teams have used mesh networks well during disasters. For example, in California wildfires, these networks helped connect people. This connection was important for organizing firefighting efforts.
Enhancing Radio Communication Systems
Radio communication remains a reliable and critical tool for first responders, especially in areas where other technologies might fail. However, advances in radio technology have made these systems even more effective.
- Digital Radios: Digital radios offer enhanced sound quality and greater range. This makes it easier for teams to stay in contact across vast or obstructed terrains.
- Integration with Other Systems: Modern radios can now integrate with wireless networks, satellites, and other communication systems. This ensures that responders have multiple ways to connect.
Integrating Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and The RATT for Communication Relay
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, are another innovative solution for extending communication networks. In remote areas, drones can act as communication links, flying above to extend coverage where ground signals can’t reach.
UAVs offer fast deployment and can cover large areas without the need for heavy equipment. For example, during natural disasters, responders use drones to relay signals in flooded or inaccessible regions. Using drones for watching from the sky and for communication is helpful.
However, most drones depend on battery life and are subject to weather conditions. This can reduce how well they work over long-term operations.
In contrast, The RATT provides a more durable and reliable solution for communication relays in challenging environments. Designed for extended use, The RATT elevates to provide communication signals across large areas without the limitations of battery life.
The RATT serves as a mobile communication center. You can deploy it in places where critical coverage is required. This includes large events, during emergency situations, or in rural areas with weak signals.
The combination of The RATT and UAVs can create a powerful communication network. People can use drones for quick setup and short-term coverage. The RATT provides ongoing communication for long-term coverage. Together, these technologies provide both flexibility and stability, ensuring reliable communication in even the most remote or disaster-affected areas.
Training and Preparedness for Effective Remote Communication
Communication technology is only effective when first responders are properly trained to use it. Developing and maintaining skills is essential for ensuring that teams can effectively operate in remote areas.
- Regular Drills: Conducting training exercises in remote areas can help teams familiarize themselves with their equipment and practice coordinating under challenging conditions.
- Contingency Plans: Developing backup communication plans ensures that teams are prepared to respond even if their primary systems fail. This might include portable satellite devices, a cache of two-way radios, extra batteries, or manual communication methods like signal flares.
Conclusion
For first responders, maintaining communication in remote areas is a complex but essential requirement. Teams can use wireless technology, mobile surveillance systems, telescopic masts, mesh networks, drones, and improved radios. These tools help them address challenges in the field posed by weather, difficult terrain and poor infrastructure. With good training and preparation, first responders can always be ready to communicate well, no matter where they are.